Join Cardinality Estimation using Histogram Coarse Alignment

How the new SQL Server cardinality estimator uses histogram coarse alignment.


How the new SQL Server cardinality estimator uses histogram coarse alignment.

A redundant and problematic TOP (1) added to the inner side of an apply anti join.

An anti join does not automatically come with a 'row goal'. This article describes anti joins and the conditions required for the optimizer to add a row goal.

When the SQL Server query optimizer adds a row goal for a semi join. How you can spot the effects in showplan and trace flag output.

Information about SQL Server row goals and why they're important when trying to understand why the query optimizer made a particular choice.

Using character substrings (trigrams) to speed up wildcard searches in SQL Server. Provides an fairly complete example implementation.

Using a debugger to explore how SQL Server derives estimates when combining multiple single-column statistics.

Improving execution plans and performance for queries involving computed columns using a new trace flag in SQL Server 2016.

It makes sense for the optimizer to consider reordering the inputs to a concatenation when less than the full potential result set is needed. Surprisingly, SQL Server does not do this in general.

Deep dive into SQL Server temporary table and variable caching, including common misconceptions and practices that disable this optimization.
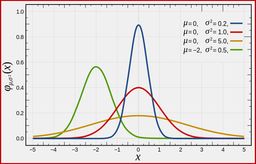
The statistical science and algorithms behind the way SQL Server calculates a cardinality estimate for a filter on a COUNT aggregate.

SQL Server sometimes produces misleading information about sort operations in execution plans.

How WITH ENCRYPTION is implemented and how to reverse it using T-SQL.

Why an update may fail when a partition has some data on a read-only filegroup due to "rowset sharing". Includes several workarounds for the issue.

The SQL Server query optimizer does not use uniqueness information obtained through automatic indexed view matching.

Follows the process of optimizing a simple update query and explores some deep internals including "lazy latches" along the way.

Optimized and static bitmap filters, null rejection, and worst-case hash join performance.

Surprising implementation details for INSTEAD OF triggers and a cardinality estimation bug in SQL Server 2014 onwards.